orbital floor fracture complications
Orbital floor fracture. Inside the skull the base is subdivided into three large spaces called the anterior cranial fossa middle cranial fossa and posterior cranial fossa fossa trench or ditch.
How To Manage Orbital Fractures
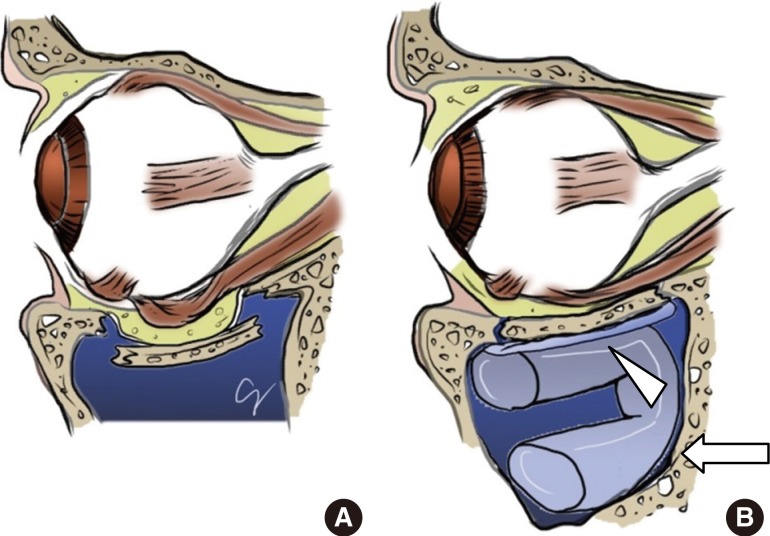
10 A similar and more popular theory is the hydraulic mechanism whereby the fracture is the result of increased intra-orbital pressure from the eye entering the orbit and not due to direct contact.

. Since many patients with maxillary sinus fractures will also have multiple other injuries it is difficult to predict. The prognosis of these patients is largely based on the severity of the injuries. Acute chronic or recurrent maxillary rhinosinusitis.
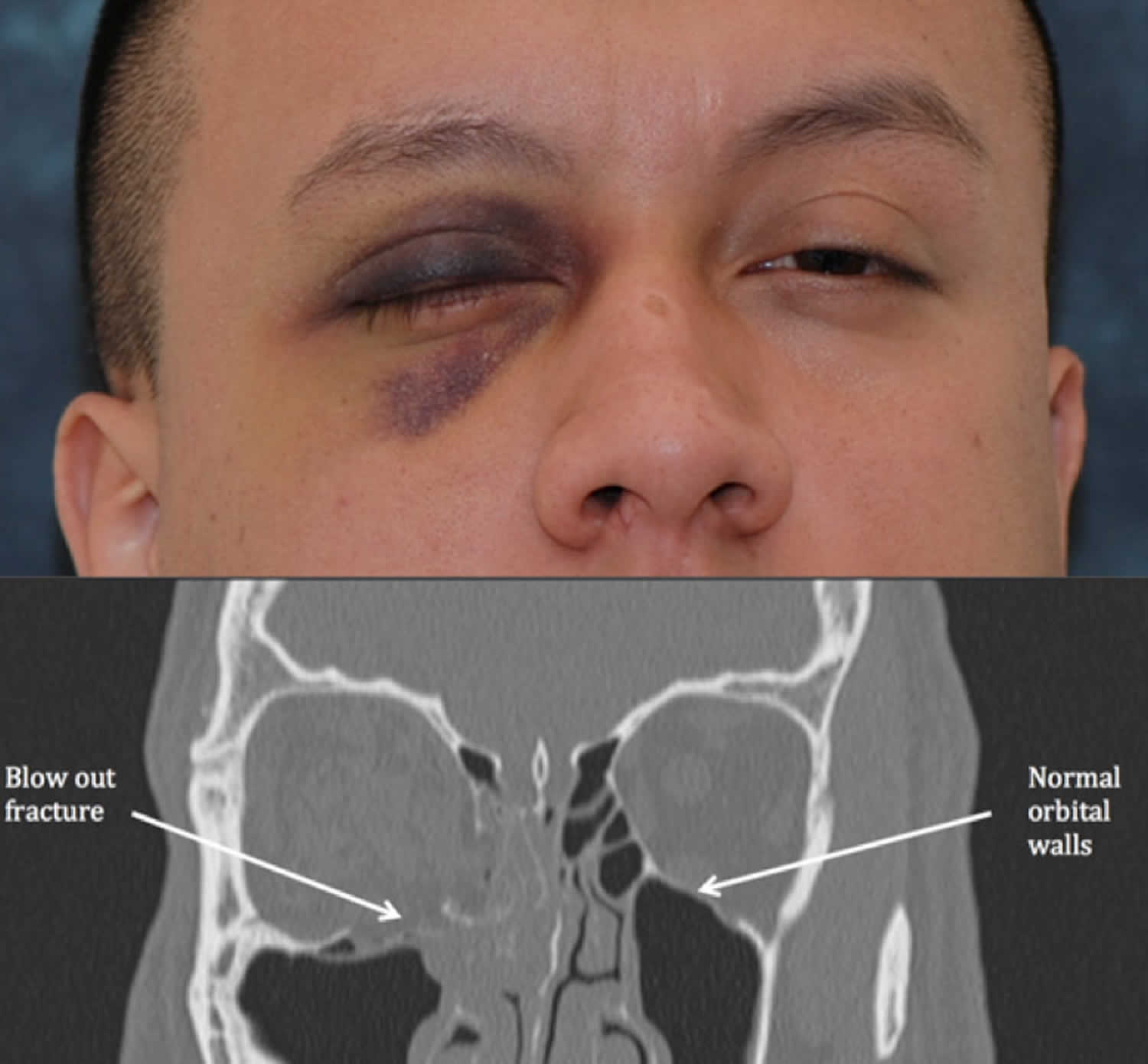
A black eye often results from injury to the face or the head and is caused when blood and other fluids collect in the space around the eye. This is a complex area that varies in depth and has numerous openings for the passage of cranial nerves blood vessels and the spinal cord. The International Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons IAOMS is the largest not-for-profit professional association representing oral and maxillofacial surgeons worldwide.
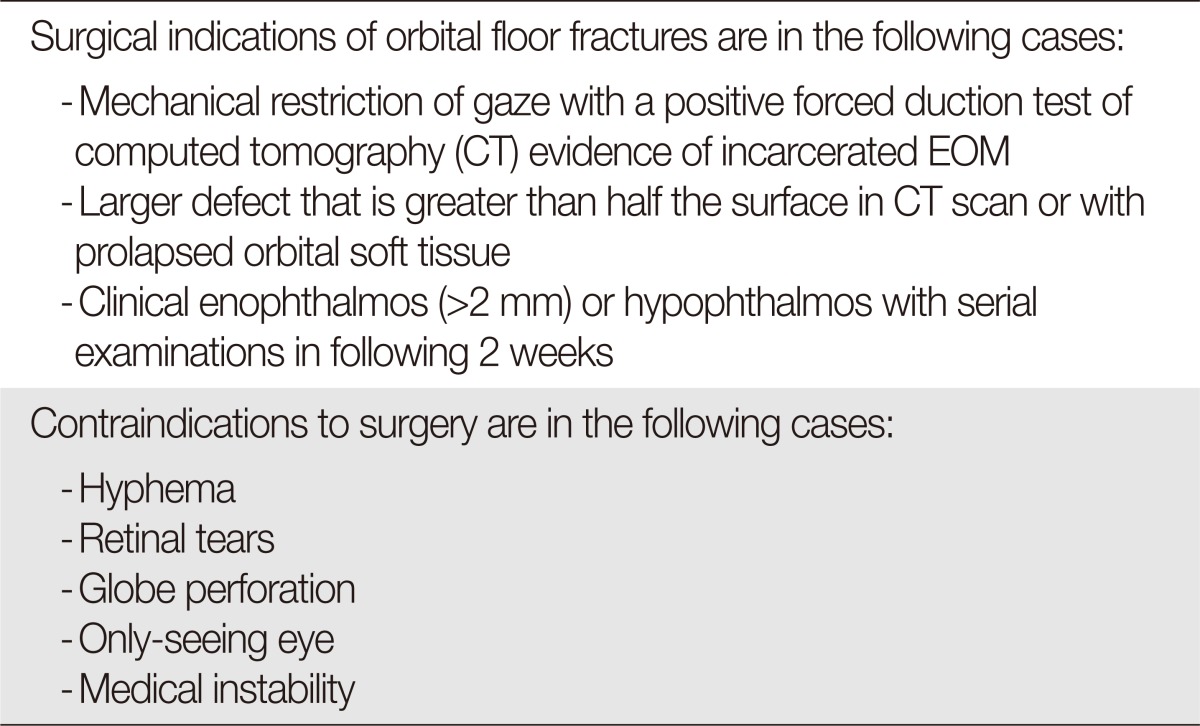
Complications include traumatic iritis and uveitis hyphema glaucoma orbital floor fracture blowout fracture and retinal detachment. The floor of the brain case is referred to as the base of the skull. The American Journal of Ophthalmology is a peer-reviewed scientific publication that welcomes the submission of original previously unpublished manuscripts directed to ophthalmologists and visual science specialists describing clinical investigations clinical observations and clinically relevant laboratory investigations.
Our mission is to elevate the quality and safety of healthcare worldwide through the advancement of patient care education and research furthering the art and science of oral and. Pfeiffer proposed the Globe-to-Wall Theory which is when a force pushes the globe into the orbit and causes the globe to contact the orbital floor resulting in a floor fracture. Facial hematoma or contusion.
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocraniumIt is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front in front of the basilar part of the occipital boneThe sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbitIts shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended. Swelling and dark discoloration result in a.

Fractures Involving Bony Orbit A Comprehensive Review Of Relevant Clinical Anatomy Sciencedirect

Orbital Floor Fractures Ento Key
Learningradiology Blowout Blow Out Fracture Orbit

A Case Of Combined Orbital Floor And Medial Wall Fracture A 44 Year Old Download Scientific Diagram
Orbital Reconstruction For Orbit Orbital Floor Fracture

Orbital Fracture Repair Plastic Surgery Key
Orbital Floor Fracture Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis